When applying for a personal loan, you may hear terms like credit score, salary slips, debt, or EMI history. But one term that people often overlook—yet banks rely on heavily—is the Loan-to-Income Ratio (LTI). Even if your credit score is strong and your salary is stable, your loan approval can still get rejected if your LTI ratio is too high.
So, what exactly is this ratio, why does it matter, and how can you improve it?
Let’s break it down in a simple, friendly, and fully humanized way.
What Is the Loan-to-Income (LTI) Ratio?
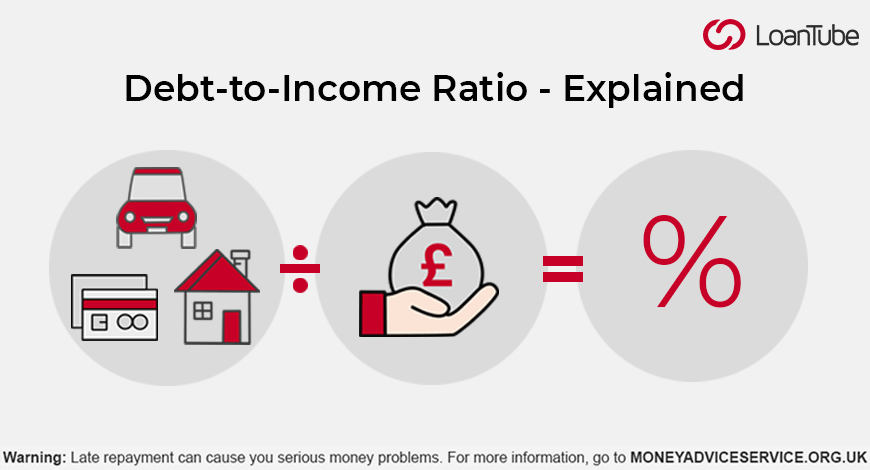
The Loan-to-Income Ratio measures how much of your total income is already committed to existing loans. In simple words:
👉 It shows how much you owe compared to how much you earn.
Lenders use this calculation to check whether you can afford another loan without financial stress.
Formula:
LTI Ratio = Total Outstanding Loan Amount / Annual Income
For example:
If you earn Rs. 1,200,000 per year and have a total ongoing loan of Rs. 400,000, your LTI ratio is:
400,000 / 1,200,000 = 0.33 (or 33%)
This means 33% of your income is already committed to debt.
Why Lenders Care About Your LTI Ratio
Banks and financial institutions want to ensure you don’t fall into a repayment trap. Here’s why the LTI ratio matters to them:
1. Measures Your Ability to Repay
If you already have too much debt, another loan increases the risk of default.
A high LTI ratio signals financial pressure.
2. Helps Predict Risk
Lower LTI ratio = lower risk
Higher LTI ratio = higher risk
Lenders prefer customers who can repay comfortably—even in emergencies.
3. Decides Loan Approval
Even if your documents are perfect, a very high LTI ratio can result in:
❌ Loan rejection
❌ Lower loan sanction
❌ Higher interest rate
4. Impacts EMI Affordability
If your income is already tied up in EMIs, taking another loan can increase your burden.
Banks want to ensure you won’t struggle.
What Is an Ideal Loan-to-Income Ratio?
Most lenders prefer when your total loan burden stays within safe limits.
Common LTI Benchmarks:
-
0% to 20% — Excellent
-
20% to 40% — Acceptable
-
40% to 60% — Risky
-
60%+ — Very high chance of loan rejection
Banks generally want your LTI ratio below 40% for smooth approval.
How LTI Ratio Impacts Your Personal Loan
Your LTI ratio directly affects almost every step of getting a personal loan:
1. Loan Approval Decision
If your LTI ratio is too high, banks may think you are already overloaded with EMIs and might reject your application.
2. Loan Amount Sanctioned
Even if approved, a high ratio may reduce your eligibility.
Example: Instead of Rs. 500,000, the bank may approve only Rs. 250,000.
3. Interest Rate Offered
Borrowers with lower LTI ratios often receive:
✔ Lower interest rates
✔ Better repayment terms
✔ Higher loan amounts
4. EMI Flexibility
Lower LTI means you can choose:
-
Comfortable EMI plans
-
Shorter or longer tenure
-
Lower monthly burden
Factors That Increase Your LTI Ratio
If your ratio seems high, here are the common reasons:
1. Multiple Loans at the Same Time
Personal loan + bike loan + mobile financing + credit card EMIs = large debt load.
2. High Credit Card Usage
Even if you pay on time, high balances increase your debt count.
3. Low Income Compared to Obligations
A smaller salary makes every EMI feel heavier.
4. Short Loan Tenure
Shorter terms have bigger EMIs, which increases your ratio.
How to Lower Your Loan-to-Income Ratio
If your LTI ratio is too high, the good news is—you can improve it. Here’s how:
1. Pay Off Small Loans First
If you have:
-
Mobile phone EMIs
-
Small consumer loans
-
Buy-now-pay-later payments
Clearing these quickly reduces your debt percentage.
2. Increase Your Monthly Income
Even a small increase in income significantly improves LTI calculations.
You can consider:
-
Part-time freelancing
-
Online gigs
-
A salary increment request
-
Commission-based work
3. Choose a Longer Tenure
A longer loan tenure reduces EMI amount and lowers LTI ratio, making you more eligible.
4. Reduce Credit Card Usage
Try:
-
Paying full balance
-
Avoiding unnecessary swipes
-
Keeping usage below 30%
This reduces your monthly liability count.
5. Consolidate Multiple Loans
Instead of many small loans with different EMIs, take one consolidated loan to reduce the burden.
Often, this reduces LTI and simplifies planning.
6. Prepay When Possible
If you get extra income (bonus, gift, commission), use it to prepay high-interest loans.
This lowers debt and improves your LTI score instantly.
Why Understanding LTI Ratio Matters for You
Knowing your Loan-to-Income ratio helps you:
✔ Apply confidently
✔ Estimate your eligibility
✔ Avoid loan rejection
✔ Get better loan terms
✔ Plan your financial future
✔ Prevent overborrowing
It’s a simple yet powerful tool that keeps you financially safe.
Final Thoughts
Your Loan-to-Income Ratio is more than just a number—it reflects your overall financial health. Before applying for a personal loan, calculate your LTI ratio to understand where you stand. If it’s too high, take steps to reduce it. Banks appreciate borrowers who manage their credit responsibly, and a healthy LTI ratio increases your chances of smooth approvals, lower interest rates, and better loan experience.
A personal loan should help you—not add stress.
So always plan smartly, maintain a balanced debt load, and borrow only what you can comfortably repay.